How Common Is Lip Filler Migration
Book a Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Causes of Lip Filler Migration
Injection Technique
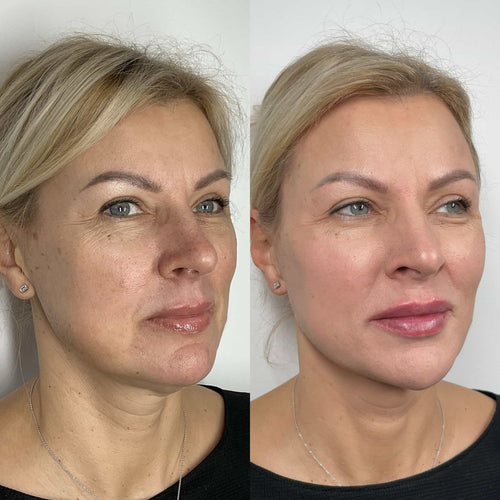
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid fillers, commonly used to enhance lip volume and shape, move from their intended location. This can result in an unnatural appearance, such as a “bubble” or lump formation, asymmetry, or blurring of the lip lines.
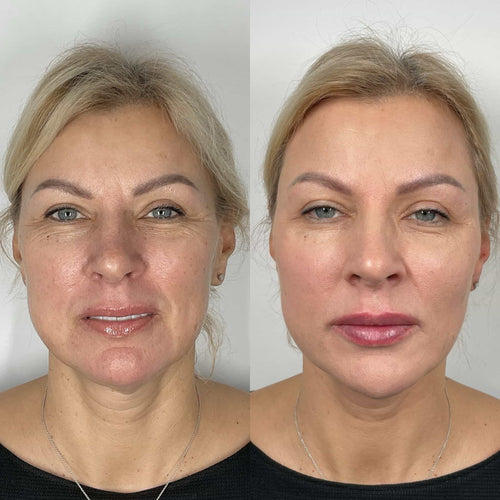
Several factors can contribute to lip filler migration:
Injection Technique: Improper injection techniques are a major culprit. Injecting too superficially, using excessive force, or not ensuring adequate spreading of the filler can lead to pooling or displacement.
Patient Habits and Activities: Certain activities and habits can increase the risk of migration. These include vigorous facial expressions, kissing, chewing on straws, and sun exposure.

Get Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Dermal Anatomy and Movement:** The lips are highly mobile structures with intricate networks of muscles and tissues. Filler placement that doesn’t account for these anatomical features can lead to movement.
Filler Type: Some fillers are formulated differently and may be more prone to migration than others. Cross-linking density, viscosity, and particle size can all influence migration potential.
Other Factors:**
Underlying skin conditions like rosacea or collagen deficiencies may affect filler longevity and stability.
Minimizing lip filler migration requires a skilled injector who understands proper injection techniques. Key aspects of meticulous injection include:
• **Careful Assessment:** Thoroughly evaluating the patient’s anatomy, desired outcome, and any potential risk factors.
• **Subtle Placement:** Injecting the filler gradually in small amounts, using a slow and steady motion to avoid excessive pressure and promote even distribution.
• **Strategic Fanning Techniques:** Spreading the filler gently along the desired area to ensure it’s evenly dispersed and not concentrated in one spot.
• Appropriate Depth:
Injecting at the correct depth for optimal results while minimizing the risk of displacement.
• **Regular Follow-Up Appointments:** Monitoring the filler over time to address any migration or adjustments needed.
Product Characteristics
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid (HA) filler, injected into the lips, moves from its intended location.
Several factors can contribute to this phenomenon:
-
Injection Technique: Improper injection techniques, such as injecting too deeply or using excessive force, can increase the risk of filler migration. Injecting into areas with thin skin or insufficient subcutaneous fat may also lead to leakage.
-
Filler Type and Viscosity: The type and viscosity (thickness) of HA filler used play a role. Some fillers are designed for specific areas and have different properties that influence their movement within the tissue.
-
Individual Anatomy and Skin Elasticity: Differences in individual facial anatomy, skin elasticity, and lip structure can affect filler migration. For example, individuals with thinner lips or less supportive tissue may be more prone to migration.
-
Excessive Expression and Movement: Frequent smiling, talking, or other facial expressions can cause filler to shift over time, especially in areas with weak muscle attachments.
-
Sun Exposure and UV Damage: Prolonged sun exposure can weaken the skin’s integrity, increasing the likelihood of filler migration.
-
Hormonal Fluctuations: Changes in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can affect collagen production and skin elasticity, potentially influencing filler movement.
Understanding these factors helps practitioners choose appropriate fillers and injection techniques to minimize the risk of migration. Patients should also follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully to optimize results and reduce potential complications.
Individual Patient Factors
Lip filler migration occurs when hyaluronic acid filler, injected into the lips to enhance their shape and volume, moves from its intended location.
Several factors can contribute to this phenomenon, both related to the injection technique and individual patient characteristics.
Injection Technique:
-
Incorrect Injection Depth: Injecting filler too superficially can increase the likelihood of migration as it’s more susceptible to spreading.
-
Improper Spreading and Placement: Inadequate distribution or uneven placement of filler can create pockets that allow for movement.
-
Overfilling: Injecting excessive amounts of filler can strain the surrounding tissues, making migration more probable.
Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Book with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Individual Patient Factors:
-
Facial Anatomy: Individuals with thin lips, prominent lip lines, or less defined muscle structure may be more prone to filler migration due to the looser architecture of their facial tissues.
-
Skin Elasticity: Those with thinner, less elastic skin are more susceptible to filler movement as the skin loses its ability to hold the filler in place.
-
Muscle Movement: Active lip movements, such as talking, smiling, or kissing, can contribute to filler migration over time.
-
Smoking and Sun Exposure: These habits degrade collagen and elastin, weakening the skin and increasing the risk of filler migration.
-
Age: As we age, our skin loses its natural plumpness and elasticity, making it more vulnerable to filler movement.
Understanding these factors can help both patients and practitioners make informed decisions about lip filler injections and minimize the risk of migration.
Symptoms of Lip Filler Migration
Asymmetrical Lips
Lip filler migration is when the injected hyaluronic acid gel moves from its original placement in the lips.
This can happen for a variety of reasons, including improper injection technique, excessive movement or expression after treatment, and certain individual factors like skin elasticity and metabolism.
Recognizing the symptoms of filler migration is crucial for early intervention and preventing potential complications.
One common symptom is an uneven appearance of the lips.
The injected filler may bunch up or collect in unexpected areas, creating asymmetry or distortions in lip shape.
For example, you might notice one lip appearing fuller than the other, a noticeable “lump” or bump on a particular area of the lips, or a distorted Cupid’s bow (the indentation above the lip).
Another sign is the appearance of filler in unintended areas.
Hyaluronic acid can sometimes migrate into surrounding tissues, causing it to appear as swelling or a raised area around the mouth.
It’s important to remember that initial bruising and swelling after lip filler are normal and should subside within a few days.
However, if you notice any persistent asymmetry or unusual lumps that don’t resolve, consult with your injector immediately.
Promptly addressing filler migration can often result in its correction or dissolution through the use of hyaluronidase, an enzyme that breaks down hyaluronic acid.
Filler Bunnies or Nodules
Lip filler migration, also known as “filler bunnies” or “nodules,” is a cosmetic concern that can occur after lip augmentation with dermal fillers.
Symptoms of lip filler migration typically appear days to weeks after the injection procedure.
Common symptoms include:
- Visible lumps or bumps along the lips, often resembling small beads or “bunnies.”
- Asymmetry or unevenness in the shape of the lips.
- A feeling of fullness or tightness in the injected area.
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling around the filler.
- Redness or discoloration at the injection site.
-
Asymmetry: Noticeable differences in the shape or size of your upper and lower lips.
-
Distorted Lip Lines: Blurred, uneven, or indistinct Cupid’s bow or vermillion border (the line that separates the pink part of your lip from your skin).
-
Lumpy or Nodular Appearance: Visible bumps or lumps under the skin of your lips.
-
Filler “Pooling” in Undesired Areas: The filler may gather in unintended spots, like the white roll (the thin strip along the inside of your lip) or above the Cupid’s bow.
-
Lip Swelling and Tenderness: Increased swelling or discomfort around the treated area.
-
Choose a qualified and experienced injector: A skilled practitioner with expertise in dermal fillers, particularly those specific to the lips, is crucial. They understand proper injection depths, techniques, and anatomical considerations.
-
Thorough consultation: Discuss your medical history, any allergies or medications you take, and your desired outcome. This helps the injector assess potential risks and tailor the procedure accordingly.
-
Use high-quality fillers:
-
Opt for hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers from reputable manufacturers with a proven track record. HA fillers are generally safer and more reversible than other types.
-
Consider the filler’s cross-linking density: Less cross-linked HA fillers tend to be softer and more mobile, potentially leading to less migration.
-
Appropriate injection technique:
-
Precise placement is key. Avoid injecting too superficially or deeply. Injectors use specific cannulas or needles designed for lip augmentation to minimize trauma and promote even distribution.
-
Spreading the filler evenly: Distribute the product gradually and strategically, avoiding large, concentrated injections that can increase the likelihood of migration.
-
Adhere to post-injection instructions:
-
Follow your injector’s specific aftercare guidelines, which may include:
-
Avoiding strenuous activity and heat exposure for a few days to reduce inflammation and swelling.
-
Applying ice packs as directed to minimize bruising and discomfort.
-
Keeping the injection area clean and avoiding touching or rubbing it excessively.
-
Massage therapy: Gentle massage techniques may help redistribute the migrated filler.
-
Dissolving the migrated filler: If necessary, your injector can inject hyaluronidase, an enzyme that breaks down HA fillers.
The migrated filler may shift from its intended location, forming irregularities in the lip contour. This can result in an unnatural or distorted appearance.
Filler bunnies typically appear as small, movable bumps that feel hard to the touch. They often resemble tiny beads and tend to form near the injection sites.
Nodules, on the other hand, are larger and more firm than filler bunnies. They can be painful or tender to the touch and may take longer to resolve.
Blurred Lip Lines
Lip filler migration occurs when the injected hyaluronic acid gel, used to enhance lip volume, moves from its original placement.
This can happen due to various factors, including improper injection techniques, excessive movement of the lips after treatment, or natural breakdown and absorption of the filler.
Here are some symptoms of lip filler migration:
Blurred lip lines are a common symptom of filler migration. This occurs when the hyaluronic acid gel moves outward from its intended placement, disrupting the natural definition of the lip border.
The result can be an appearance of “stretched” or uneven lips that lack clear definition.
Preventing and Addressing Migration
Proper Injection Techniques
Lip filler migration is a concern that arises when injected dermal fillers move from their intended location, causing lumps or unevenness. Understanding the causes and preventative measures can help minimize this risk.
Several factors contribute to lip filler migration. One primary cause is improper injection technique. Injecting too deeply, using excessively large needles, or not dispersing the filler evenly can increase the likelihood of displacement.
Another factor is the patient’s individual anatomy and physiology. Skin elasticity, facial musculature, and underlying fat deposits can influence filler movement. Patients with thinner skin or more mobile lips may be more susceptible to migration.
Certain fillers are formulated to have greater cohesiveness and stability, reducing the risk of migration compared to others. Hyaluronic acid-based fillers, for instance, are generally considered less prone to migration than other types of fillers.
Proper injection techniques are crucial in preventing filler migration. Here’s a breakdown of best practices:
1. **Consultation and Assessment:** Thoroughly assess the patient’s facial structure, skin type, desired outcome, and medical history to determine the appropriate type and amount of filler.
2. **Anesthesia:** Utilize topical anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and minimize discomfort during injections.
3. **Injection Technique:**
* Use a small needle gauge (25-30) for precise placement and reduce trauma to the tissues.
* Inject gradually in multiple, shallow passes, gently dispersing the filler along the desired contours.
* Avoid injecting directly into muscle bellies or areas of excessive motion, which can increase the risk of migration.
4. **Massage and Pressure:** After injection, gently massage the treated area to help distribute the filler evenly and minimize lumpiness.
5. **Post-Injection Care:** Advise patients on post-injection care, including avoiding strenuous activity, direct sunlight exposure, and rubbing or touching the treated area for several days.
Addressing Lip Filler Migration
If lip filler migration occurs, treatment options include:
1. **Dissolving the Filler:** Hyaluronidase, an enzyme, can be injected to break down hyaluronic acid-based fillers and relocate them.
2. **Massage and Redistribution:** In some cases, gentle massage may help reposition the migrated filler.
3. **Surgical Excision:** If the migrated filler is significant or causing persistent problems, surgical removal may be necessary.
Prevention is always better than cure. By understanding the factors that contribute to lip filler migration and employing proper injection techniques, healthcare professionals can minimize risks and ensure safe and aesthetically pleasing results for their patients.
Choosing Reputable Injectors
Lip filler migration is a recognized complication that can occur after hyaluronic acid (HA) filler injections. It involves the movement of the filler material from its intended location, often resulting in an asymmetrical or undesirable appearance.
Preventing migration primarily focuses on careful injection techniques and patient selection. Experienced injectors use specific techniques, such as precise placement, fanning out the product, and using a blunt cannula instead of a needle, to minimize the risk of spreading.
Choosing reputable injectors is paramount in preventing complications like migration. Look for practitioners with extensive experience in facial injectables, particularly lip augmentation. They should be board-certified or licensed in their field and maintain up-to-date knowledge on best practices and safety protocols.
Patients can also play a role in prevention by:
• Following pre-injection instructions carefully, such as avoiding blood thinners
• Disclosing any medical conditions or allergies to the injector
• Understanding potential risks and complications beforehand.
Addressing migration often requires additional treatment. Depending on the severity and location, options include:
• Hyaluronidase injections to break down the migrated filler
• Massage techniques to redistribute the filler
• Revision surgery in some cases.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified injector if you notice any signs of migration, such as asymmetry, bumps, or distortion. Timely intervention can help minimize the impact and achieve better aesthetic outcomes.
Post-Injection Care
Lip filler migration is a recognized complication that can occur after dermal filler injections. While it’s not always easy to prevent entirely, understanding the factors contributing to migration and implementing proper injection techniques can significantly reduce the risk.
Here’s a breakdown of preventive measures and post-injection care strategies for managing lip filler migration:
Prevention
Post-Injection Care
If you notice any signs of filler migration after your procedure, such as unevenness, lumps, or movement of the filler beyond its intended location, consult your injector immediately. They can assess the situation and determine the best course of action, which may include:
- Brow Lift Treatment Near Purley, Surrey - May 8, 2025
- DIY Kratom Energy Drinks: Recipes And Tips - May 8, 2025
- How Long After Lip Filler Can You Get Lip Blush - May 7, 2025

